Your Location:Home > Products > ANTI-AGING > Nicotinamide Riboside
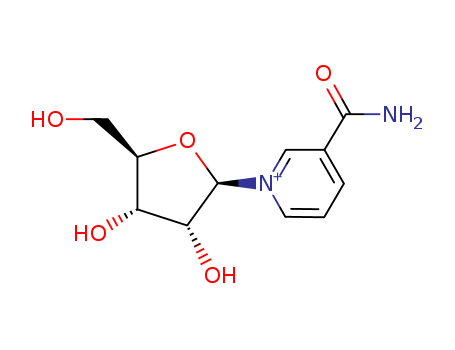


CasNo: 1341-23-7
MF: C11H15 N2 O5
|
benefits |
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is one of the viable natural precursors for the biosynthesis of NAD+ via two alternative pathways involving the purine nucleoside phosphorylase or the nicotinamide riboside kinase enzymes. Therapeutic benefits of nicotinamide riboside supplementation:Constant dietary supplementation of nicotinamide riboside has been shown to increase the NAD+ levels in middle aged to elderly people.It may support mitochondrial function.It may enhance memory and combat cognitive decline.It might lengthen your life.It might promote muscle quality and strength.It might counter the effects of a high-fat diet.In 2016 NR received the GRAS (Generally Recognized As Safe) status from the FDA. NR also demonstrated the potential to slow aging processes in mice models. |
|
Biological Functions |
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a critical coenzyme that, when reduced to NADH, serves as a reducing agent to donate electrons for oxidative phosphorylation and ATP synthesis in mitochondria. NAD+ is a critical cofactor for enzymes such as sirtuins, ADP-ribosyltransferases (ARTs), and Poly [ADP- ribose] polymerases (PARPs) and is continuously consumed by these enzymes. The NAD+/NADH ratio is a critical component of the redox state of the cell. (Verdin 2015). By some counts, NAD or the related NADP participates in a quarter of all cellular reactions (Opitz Heiland 2015). There are separate compartments of NAD+ in the nucleus, mitochondria, and cytoplasm (Verdin 2015). Nicotinamide riboside (NR) can be converted into NAD+ through an intermediate step in which it is converted into nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) by NR kinase (Nrk) and then to NAD+ by NMNATs. NR is naturally found in some foods but at very low quantities (e.g. low micromolar range). Historically, NR was difficult to obtain in large purified amounts, but thanks to advances in synthesis methods (Yang 2007), as of June 2013, it is sold as a dietary supplement. |
|
Side effects |
No serious adverse effects have been reported in human studies, though most of the studies so far have been short in duration and low in participant numbers. The need for larger scale and more robust human studies is critical if NR is to be properly evaluated.To date, some people have reported mild to moderate side effects, including nausea, fatigue, headaches, diarrhea, stomach upset and indigestion. While that seems to suggest NR is likely safe, the lack of large scale long-term studies means that this cannot be confirmed.As always, if you do decide to take a NR supplement and experience any adverse effects, you should cease taking it immediately and consult your doctor. |
|
Safety |
Nicotinamide riboside has a successful New Dietary Ingredient Notification with FDA (NDIN 882) for daily recommended intake of not more than 180 mg/d.Nicotinamide riboside is generally recognized as safe (FDA GRAS Notice No. 635) for use in vitamin waters, protein shakes, nutrition bars, gum, chews, and powdered beverages. Maximum use level 0.0057% by weight. |
|
Mode of action |
NAD+ is a critical and often rate-limiting factor in many aspects of mitochondrial and cellular function including DNA repair by PARPs, widespread acetylation and epigenetic effects by sirtuins, efficient production of ATP, and other pathways (Stein & Imai 2012). NAD+ levels decline with age as does the ratio of NAD+/NADH, with numerous studies suggesting that blunting this decline with NAD+ precursors or genetic manipulations can blunt fundamental features of aging (see below). The levels also decline with the high-fat diet but increase with calorie restriction and fasting (Stein & Imai 2012), leading some to argue that it can function as a calorie restriction mimetic.www.alzdiscovery.org |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: Nicotinamide riboside is a pyridine nucleoside consisting of nicotinamide with a beta-D-ribofuranosyl moiety at the 1-position. It is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It is an orally available form of vitamin B3 and precursor of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) with potential use in the treatment of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN). |
InChI:InChI=1/C11H13NO3/c13-10(6-7-12-8-11(14)15)9-4-2-1-3-5-9/h1-5,12H,6-8H2,(H,14,15)
A new two-step methodology achieves ster...
Haemophilus influenzae is a major pathog...
The invention discloses a preparation me...
The present invention relates to Nicotin...
The invention provides a chemical synthe...
The invention discloses a crystal form 1...

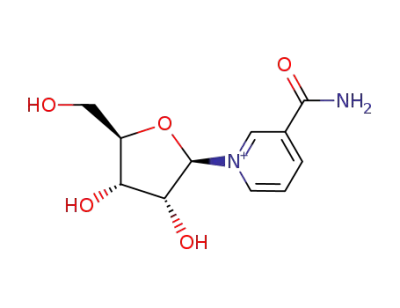
1-(β-D-ribofuranosyl)-nicotinamide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
NMN+ (oxyd. Nicotinamid-mononucleotid), enzymatische Bldg.;
|
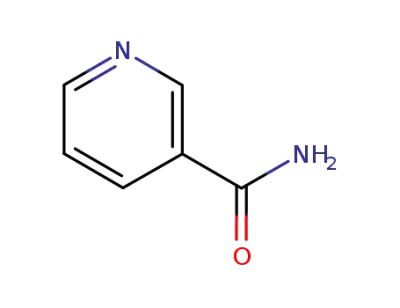
nicotinamide
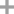
1,2,3,5-tetraacetylribose


1-(β-D-ribofuranosyl)-nicotinamide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
nicotinamide; 1,2,3,5-tetraacetylribose;
With
trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate;
In
acetonitrile;
at 20 ℃;
for 1.5h;
With
methanol;
at 20 ℃;
for 1h;
|
|
|
nicotinamide; 1,2,3,5-tetraacetylribose;
With
trimethylsilyl trifluoromethanesulfonate;
In
dichloromethane;
at 30 - 40 ℃;
Large scale;
With
potassium carbonate;
In
dichloromethane;
at 15 ℃;
for 1h;
Large scale;
|

nicotinamide

1,2,3,5-tetraacetylribose
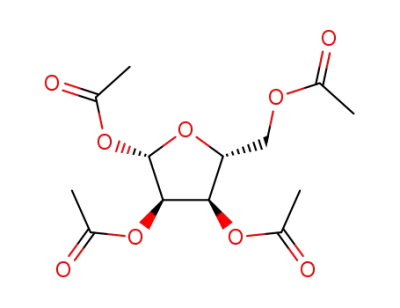
2',3',5'-triacetyl ethyl nicotinate riboside
NAD

nicotinamide
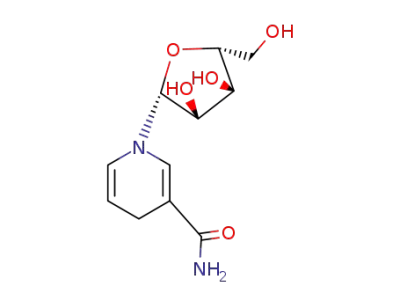
1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofur-2-yl]-1,4-dihydropyridine-3-carboxamide
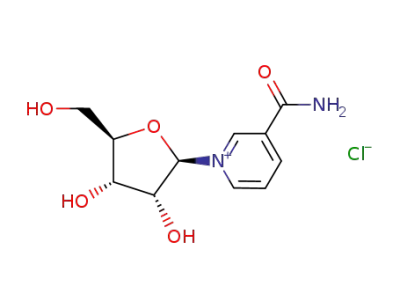
3-carbamoyl-1-((2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl)pyridin-1-ium (β-D-nicotinamide riboside)
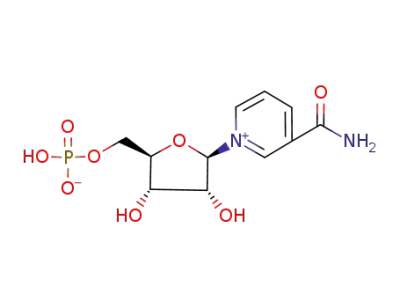
nicotinamide mononucleotide