Your Location:Home > Products > Amino Acids > L-Norvaline


CasNo: 6600-40-4
MF: C5H11NO2
Appearance: white to light yellow crystal powder
|
benefits |
Some benefits with taking L-norvaline:L-Norvaline increases blood flow to working muscles, which can lead to greater muscle pumps during workouts, less soreness after workouts, and faster recovery times between workouts.L-Norvaline, an amino acids supplement for men, may support nitric oxide production in healthy individuals, where nitric oxide plays an important role in many biological processes in the body including muscular contraction, blood circulation and blood flow throughout the body. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
L-Norvaline enhances NO production from activated macrophages. |
|
Side effects |
Mild gastrointestinal symptoms such as stomach irritation, nausea, and vomiting may result from L-Norvaline supplementation. |
|
Safety |
Researchers from the University of Technology Sydney found taking the amino acid L-norvaline, even in small doses, could make cells unhealthy and eventually kill them.However, in a study published in the US National Library of Medicine National Institutes of Health dated December 17, 2019, and entitled “Reports of L-Norvaline Toxicity in Humans May Be Greatly Overstated”, it was argued that the quantities of L-Norvaline used in the study claiming its toxicity was greatly above cytotoxic levels for all amino acids. Hence, it was concluded in the said study that as long as L-Norvaline is taken within recommended doses, it will not necessarily cause cytotoxic effects. A typical dose of L-Norvaline is around 100mg-250mg per day. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise norvaline from aqueous EtOH or water. [Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 2390-2399 1961, Beilstein 4 III 1331-1333, 4 IV 128, 2629.] |
|
General Description |
L-Norvaline is a non-proteinogenic amino acid with the chemical name (S)-2-aminopentanoic acid, characterized by a five-carbon side chain. It has been synthesized stereoselectively through efficient, chromatography-free methods, demonstrating its relevance in organic and bioorganic chemistry. L-norvaline's structural features, such as its side chain length, influence molecular interactions, as seen in studies on peptide nucleic acids (PNAs), where norvalyl derivatives were used to investigate pairing selectivity and stacking properties. This highlights its utility in designing modified biomolecules for applications in molecular recognition and synthetic biology. |
|
Definition |
ChEBI: L-Norvaline is a 2-aminopentanoic acid that has S-configuration. It has a role as a bacterial metabolite. It is a (R)-fenbuconazole and a 2-aminopentanoic acid. It is an enantiomer of a D-2-aminopentanoic acid. It is a tautomer of a L-2-aminopentanoic acid zwitterion. |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H11NO2/c1-2-3-4(6)5(7)8/h4H,2-3,6H2,1H3,(H,7,8)/t4-/m0/s1
Enzymatic electrosynthesis is a promisin...
The active site is the common hotspot fo...
ω-Transaminase (ω-TA) is an important en...
Two biocatalytic reactions, transaminati...
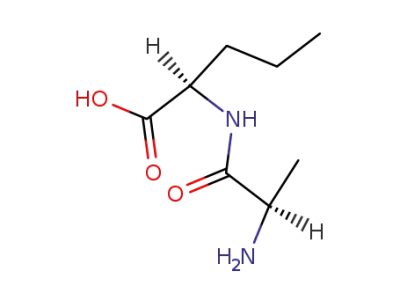
DL-α-alanyl-DL-norvaline

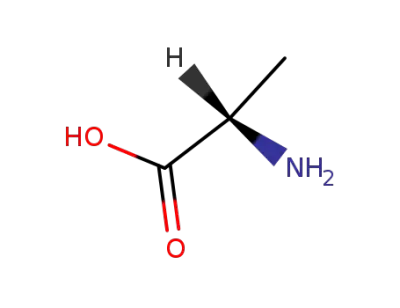
L-alanin
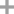
D-Alanine

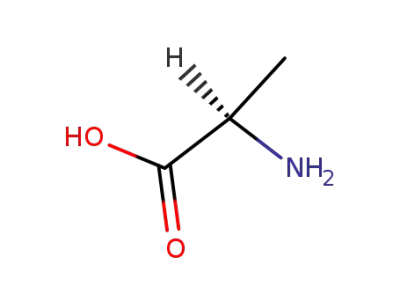
D-norvaline

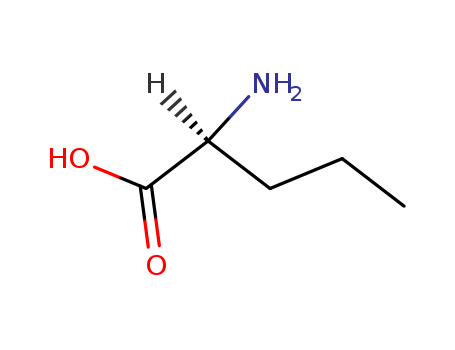
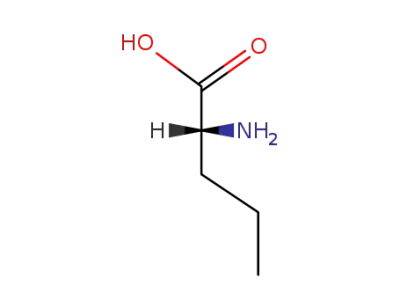
L-Norvaline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
(S)-1-(N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)-2-formylcymantrene; sodium methylate; copper (I) acetate;
for 1h;
Ambient temperature;
|
21.69% 39.43% 60.57% 78.31% |
|
With
(S)-1-(N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)-2-formylcymantrene; sodium methylate; copper (I) acetate;
for 3h;
Ambient temperature;
|
76.83% 23.15% 26.2% 73.8% |
|
With
(R)-1-(N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)-2-formylcymantrene; sodium methylate; copper (I) acetate;
for 1h;
Ambient temperature;
|
26.8% 57.84% 42.16% 73.2% |
|
With
(R)-1-(N,N-dimethylaminomethyl)-2-formylcymantrene; sodium methylate; copper (I) acetate;
for 1h;
Ambient temperature;
|
26.8% 73.2% 42.16% 57.84% |
![(2S)-[(1'R)-phenylethylamino]-4-pentenoic acid](/upload/2025/12/b0bdebe9-92a5-477a-aded-1bb50e362d25.png)
(2S)-[(1'R)-phenylethylamino]-4-pentenoic acid


L-Norvaline
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
hydrogen;
palladium on carbon;
In
water;
at 50 ℃;
for 47h;
under 16501.7 Torr;
|
41.5% |
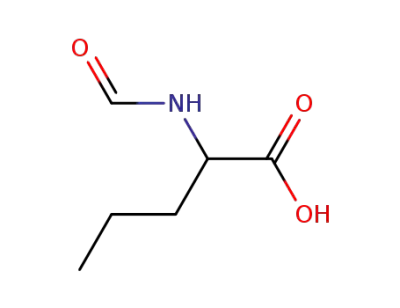
N-formyl-D,L-norvaline
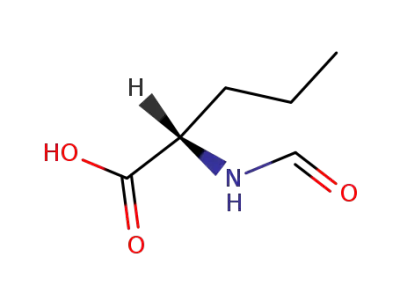
N-formyl-L-norvaline
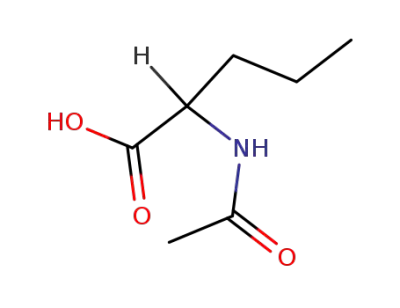
N-acetylnorvaline
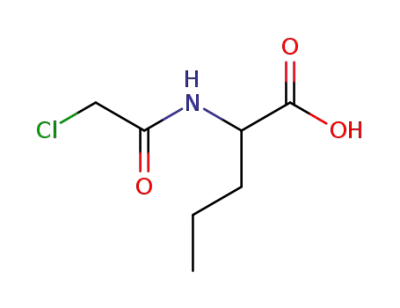
N-Chloroacetyl norvaline
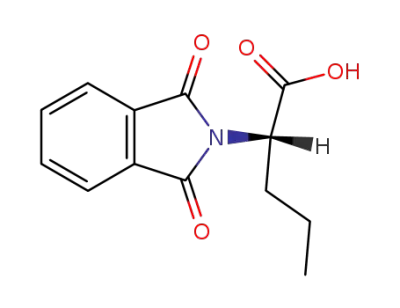
(S)-2-(1,3-dioxoisoindolin-2-yl)pentanoic acid
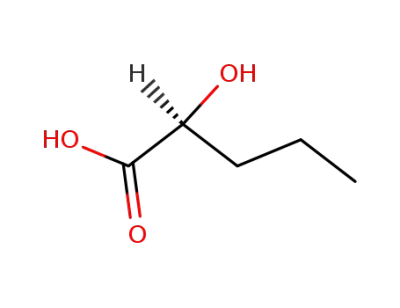
2-(S)-hydroxyvaleric acid
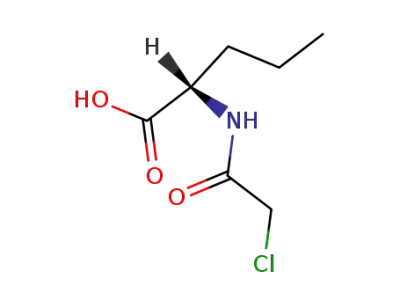
N-chloroacetyl-L-norvaline
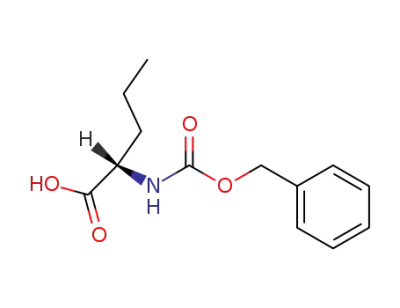
Z-L-norvaline